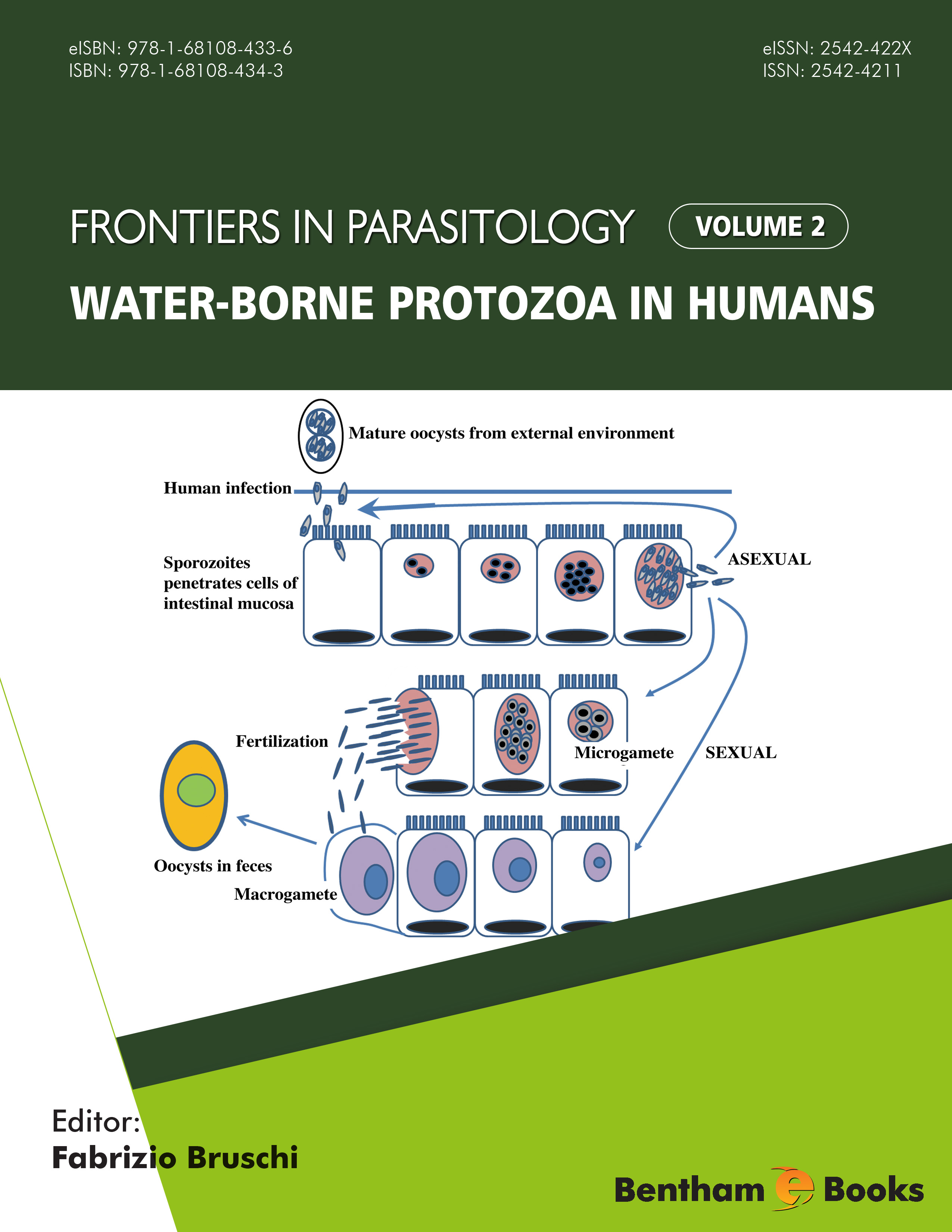
Introduction
Several parasites are able to spread diseases through contaminated water. While the spread of diseases through contaminated water appears to have a greater correlation with a lack of access to clean water in low income populations in developing countries, there have been outbreaks of water-borne diseases in developed countries. Therefore, addressing water-borne diseases is a major public health concern worldwide. Water-borne Protozoa in Humans is a guide to protozoan infections linked to contaminated water.
Each chapter of this monograph covers the history, morphology, life cycle, global epidemiology, risk factors, immunology, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and perspectives of control for each relevant protozoan parasite that can be found in contaminated water. These include Giardia duodenalis, Cryptosporidium, Free-living amoebae, Entamoeba histolytica/dispar and other pathogenic intestinal amoebae, Cystoisospora belli, cyclospora, microsporidia, and Blastocystis hominis.
This monograph is suitable for a broad readership which includes medical students, parasitologists, clinical microbiologists, epidemiologists, environmental health and water safety technicians, and public health personnel.